In 2020, the world stopped due to an outbreak of COVID-19. Around the world, journalists and scientists tried to simplify scientific expressions, such as viruses and vaccines, into simple ideas that everyone could grasp. People worldwide may now recognize the immune system as our body’s police force, which exists to fight invaders, as a virus. However, this immune-police force can help to fight not only outside invaders but also inside intruders, including cancer.
But how?
In a very similar way to how the immune system identifies a virus through antigens. These are proteins that are usually not present in our body, hence they are seen as external invaders. Do you remember the spike proteins? That’s it, a protein present in the COVID-19 virus, which we used to produce vaccines. The spike proteins are detected by our immune system as antigens, activating our police system to fight COVID-19.
Now the tricky part is, cancer cells, despite coming from healthy cells that we have in our bodies can also have proteins that we usually do not have, for instance, cancer cells can modify the proteins they produce (we have a really cool post explaining how cells produce proteins- What If a Cell Was a city? – The Industry of Protein Production). Thus, cancer cells have antigens that can activate the immune system against cancer, like traces that our police forces can follow to find the invader.
So why do we have cancer?
Although our immune defenses can kill cancer cells in the beginning of their conversion to the criminal side, often cancer cells act like true crime experts and learn ways to hide their antigen traces, becoming invisible to our immune-police forces and growing their gang. Here, it’s where scientists come with their police academy to train more and better police agents.
At this academy, immune cells are trained to better recognize and kill cancer cells, so that they can be used as treatment. To this we call: Cancer Immunotherapy. Despite just being in clinical use since the 2000s, immunotherapy is already considered the 4th pillar of cancer treatment along with surgery, chemo- and radiotherapy.
To accomplish this, in the past years, keen scientists have developed multiple police tools and trained several police agents. This is an example of the most famous agent of our immune system- T cells.
These are police agents that kill cancer cells once they recognize them by their antigens. Although efficient, for T cells to detect cancer cells, the antigens need to be presented by a specific molecule- the Major Histocompatibility complex (MHC). These MHC molecules are often decreased in cancer cells, making cancer invisible to T cells. To overcome this, T cells can be changed in the laboratory to identify cancer antigens that are not shown in these MHC molecules. We call these CAR-T cells.
Additionally, cancer cells can also arm themselves with weapons that impede T cells from killing them. For this, scientists create an antidote- proteins that cover those weapons, protecting the T cell agents and letting them do their work. The name of this antidote is immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), and it was created by James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo, who were awarded the Nobel Prize of Medicine 2018.
Many other agents are being trained in this police academy, including forensic agents (dendritic cells) whose expertise is to search for antigens and present them to T cells. Improving this police academy training is a key mission, as cancer cells can change their modus operandi. Despite the challenges, scientists around the world work daily in this mission with the belief that justice will prevail.
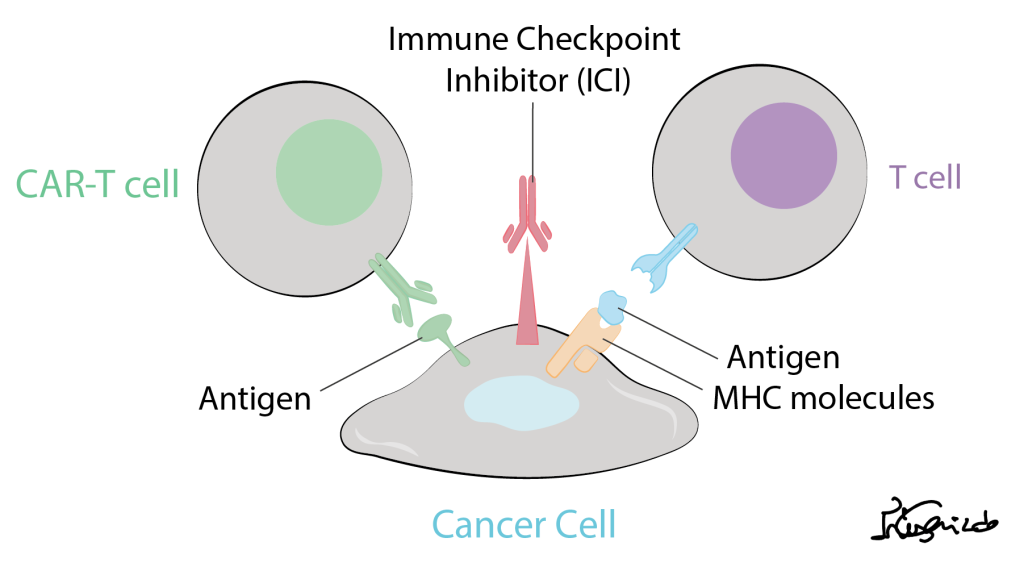
Figure 1. Cancer Immunotherapy Strategies. T cells see cancer cells by antigens shown at MHC molecules. Since cancer cells can decrease their MHC molecules, one strategy is to use CAR-T cells, which are T cell changed in laboratory to see antigens not in MHC molecules. Cancer cells can also increase molecules (immune checkpoints) that decrease T cell killing activity.To protect T cell activity, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) were created.